Improving Soil Health: An Urgent Solution for Sustainable Farming

Environmental Conditions for Caring for Newly Planted Durian Trees
a) Climate
Durian trees thrive in tropical climates with warm and humid conditions. The optimal temperature range for durian growth is 24–30°C. Extremely low or high temperatures can slow down the development of young durian trees.
The ideal humidity level is between 65–80%, with annual rainfall ranging from 1,800 to 2,000 mm. During prolonged droughts, it is essential to ensure adequate water supply, but waterlogging must be avoided to protect the root system. This means maintaining soil moisture in the dry season and ensuring proper drainage during the rainy season.
b) Soil Requirements for Durian Cultivation
Durian trees grow best in well-drained, loose, and fertile soils such as red basalt soil, alluvial soil, and light clay soil.
The soil pH should range between 4.5 and 6.5, but it is advisable to adjust the pH to 5.5–6.5 to limit the development of Phytophthora fungi, which cause root rot disease.
Step 1: Installing Support Stakes for Young Durian Trees
When transplanting young durian trees from their nursery bags to the soil, the soil should be slightly compacted around the roots but not pressed too tightly against the trunk.
A support stake should be placed alongside the main stem, and the tree should be tied to it to keep it upright, preventing wind from disturbing the roots.
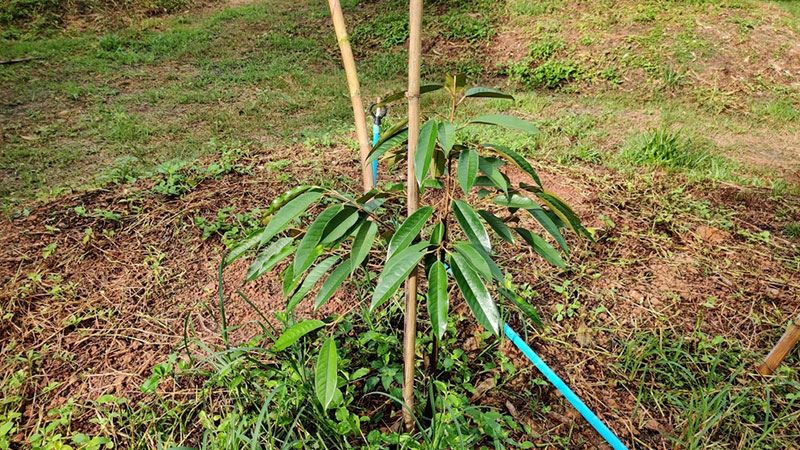

Step 2: Mulching to Retain Soil Moisture
Durian trees prefer a warm, humid climate and are sensitive to dry conditions. The ideal temperature range for durian growth is 24°C – 30°C.
After planting, farmers should mulch the soil using materials such as straw, dry branches, corn stalks, or banana stems to reduce water evaporation, retain soil moisture, and prevent soil erosion during irrigation.
⚠ Note: Keep the mulch 15–20 cm away from the tree base to prevent root rot.
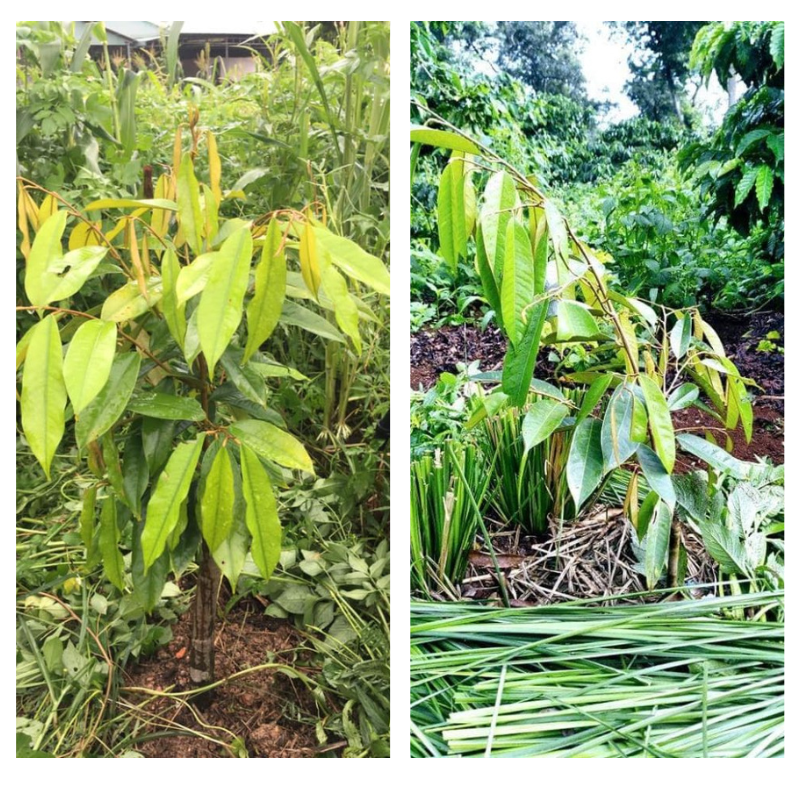

Step 3: Protecting Young Durian Trees from Sun and Wind
Durian trees require ample sunlight but should not be planted too densely to allow sufficient light for proper growth.
However, young durian leaves are delicate and can easily suffer from sunburn. During hot and sunny days, some shading may be necessary to reduce direct sunlight exposure.
Farmers can intercrop durian trees with other plants such as coffee, orange, or banana trees to provide natural shade and improve soil quality. Many durian plantations are established on land previously used for fruit or industrial crops, which may be depleted of nutrients. Intercropping helps rejuvenate the soil.

Step 4: Fertilizing Young Durian Trees
During the first week after planting, only water is needed to help the tree adapt to the soil environment.
After 7–8 days, organic microbial fertilizers should be applied, as they are easily absorbed by young trees. The fertilizer should be spread 20 cm away from the base, with a recommended amount of 1–3 kg per tree.
After 10 days (2 days after applying organic fertilizer), a root stimulant can be used to promote the development of roots, stems, and leaves.
After 10–15 days, when new shoots emerge, insecticides should be applied to prevent pests.
⚠ Fertilization Tips:
- The best time for fertilization is during spring or autumn.
- Young trees require small amounts of fertilizer, while mature trees need increased doses based on their growth stages.
- Fertilizer should be applied around the tree base rather than directly on leaves or fruits to retain soil moisture and avoid damage.
Step 5: Proper Watering Techniques
Young durian trees need a moderate amount of water to maintain soil moisture, especially during the first 45 days after planting. Underwatering can cause wilting and death, while overwatering may lead to root rot.
At the early stage, the soil moisture requirement is 65–80%. Mulching can help retain moisture. Timely and adequate watering is crucial, as insufficient moisture can hinder growth and cause plant death.
The recommended watering volume is 20–30 liters per tree per session. Proper watering encourages healthy root development and rapid establishment.
Additionally, durian trees are sensitive to stagnant water, so drainage channels must be created during the rainy season to prevent root rot and fungal diseases.

Step 6: Pruning and Canopy Formation
From an early stage, incorrect branch growth should be pruned to shape the tree structure. However, excessive pruning in nurseries should be avoided to prevent weakening the young tree.
After transplanting, canopy shaping should focus on selecting strong branches while limiting unnecessary pruning. Instead, fertilization should be prioritized to promote healthy root development.
⚠ Pruning Guidelines:
- Remove diseased, weak, or misaligned branches.
- Ensure a balanced, rounded canopy.
- Retain strong branches that can produce high yields.
- Remove excessive shoots and maintain a tree height of 5–6 meters for easier harvesting.
Step 7: Stimulating Root Growth in Young Durian Trees
Newly transplanted durian trees need time to adapt to the new environment, and their root system is still developing. Farmers should use biological root stimulants to encourage early root growth.
Timely root stimulation helps young durian trees adapt quickly, absorb nutrients efficiently, and develop strong shoots.
Step 8: Preventing Diseases in Young Durian Trees
To protect young durian trees from diseases, farmers should:
✅ Inspect the trees regularly for signs of disease.
✅ Prune branches and leaves to improve air circulation.
✅ Use insecticides when necessary to control pests.
✅ Manage the environment by ensuring proper drainage and soil health.
✅ Provide adequate nutrients to boost tree immunity.
Proper care in the early stages is crucial for the long-term success of durian trees, especially during flowering and fruit-bearing phases. If you have any questions, feel free to contact Funo's hotline at 0911311100 for expert advice!

0903.993.754 - Hotline: 0922.77.22.99
Copyright @2024 Công ty TNHH Xuất Nhập Khẩu Nông Nghiệp Goku
